Compare NBN plans and get the best Internet deals in Australia
We make it easy for you to compare NBN plans and providers. Simply enter your address to get started
At Compare Broadband, we've carefully reviewed plans from top NBN providers in Australia to give you the best advice.
Unlike others, we can help you sign up for an NBN plan directly. Contact our customer service or use our live chat to connect with a broadband expert and get started.
BENEFITS
- Find the best speed tier for your needs
- Save money and get the best deals
- Sign up for an NBN plan directly
MORE INFORMATION
- Unlimited NBN Plans
- NBN Bundles & Packages
- Business NBN Plans
- Cheap NBN Plans for Seniors & Pensioners
- What NBN speed do I need?
- How to switch NBN providers
- Why is My NBN Slow?
- NBN Outages
- How Much Does NBN Installation Cost?
- NBN Sky Muster Satellite plans
- NBN’s Fixed Wireless Connection
- NBN connection types: What’s the difference?
- How to Check NBN Speed?
- NBN FTTP Upgrade: Suburbs Eligible For Faster Internet
- The ultimate guide to your NBN connection box
- Student NBN Plans and Discounts
- Compare best NBN providers in Australia










What to consider when choosing NBN plans
Choosing the right Internet plan in Australia can be tricky with so many options to choose from. There are NBN plans best suited to families, while others match those that live alone. You can find plans with unlimited downloads, flexible contracts, and free modems. Some even include a home phone service with local and national calls.
To make a smart choice, consider these factors and how they impact your personal circumstances:
Speed
Think about your online activities and the number of devices in your household. If you spend a lot of time streaming and gaming, you'll need a faster speed tier than those who just use the Internet for basic browsing and emailing. Check the provider's advertised typical evening speed to set your expectations of what you will see during peak times.
Price
While budget-friendly plans are attractive, they may come with certain limitations, such as slower speeds. Balancing price, features, and quality is essential to meet your unique requirements. Look out for special deals that waive setup and application fees.
Support
Prioritise providers offering local support, whether that be a call centre, chat service, or self-service options. Fast and efficient customer support is invaluable for troubleshooting and resolving billing inquiries.
Moving Home
Moving home is the perfect opportunity to consider your home Internet requirements.
If you're happy with your current NBN provider, you can simply transfer your existing service to your new address. However, it's wise to explore whether you can get a better deal at your new location.
Reach out to Compare Broadband for insights into how well your current provider's services perform in your new area. And if you decide to make the switch, we're here to assist you in signing up for a new plan that suits your needs.
Popular NBN plans March 2024
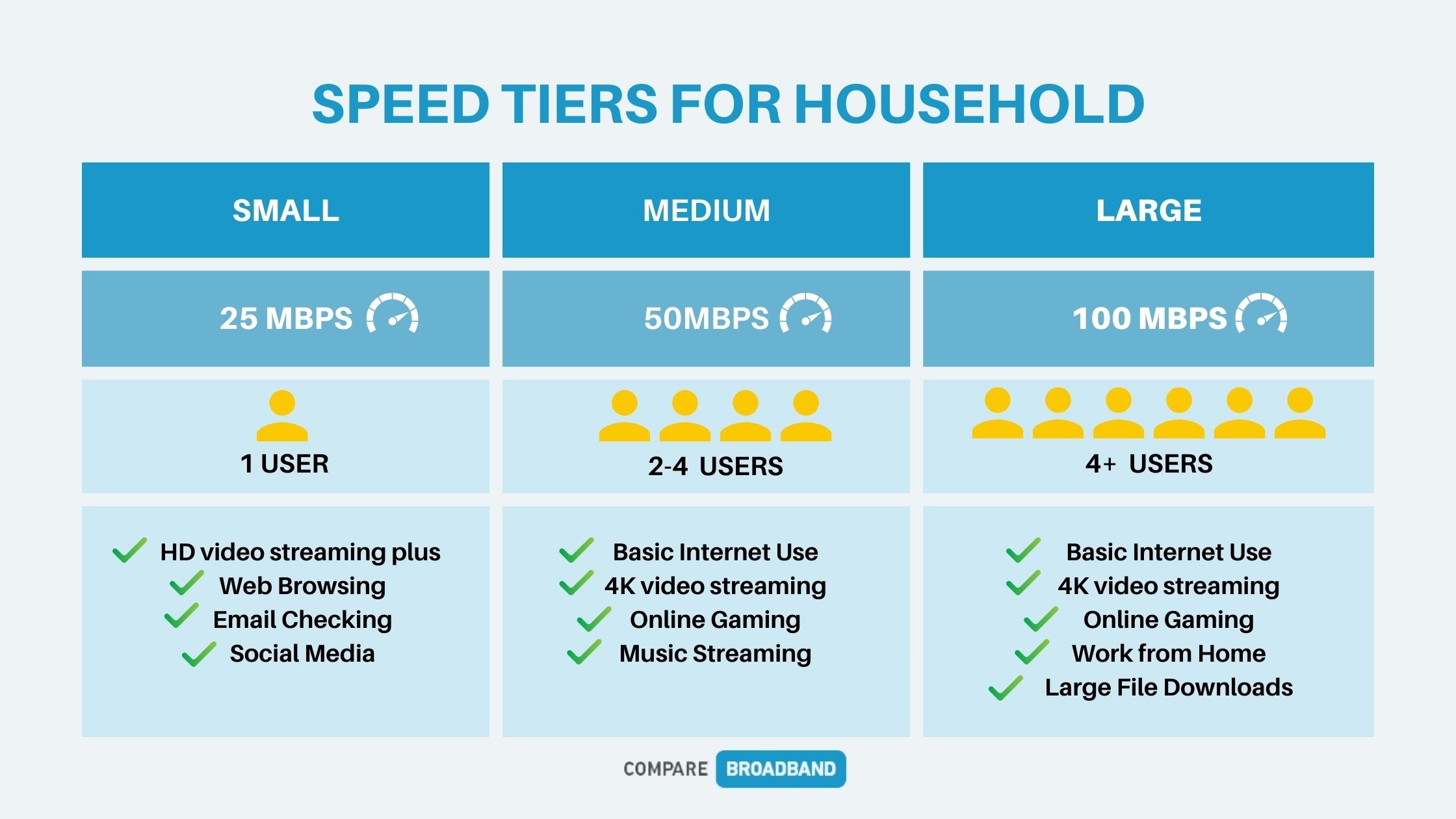
Choosing the right NBN speed tier
For residential NBN customers, there are different NBN speed tiers to consider. It's important to note that the availability of these speed options can vary based on the technology used for the NBN connection at your specific address.
NBN plans get more expensive the faster the speed tier you choose.
For many Australians, an NBN 50 plan is a solid choice with 50Mbps download speed and 20Mbps upload speed. It's good for streaming, gaming, and video calls. If you have a big household with many devices, consider faster plans for smoother performance.
Popular NBN providers
The NBN has allowed for significant growth and diversity in Internet Service Providers. To help you make informed decisions, Compare Broadband has analysed and compared leading NBN providers.
These are some of the best NBN providers in Australia right now.
Aussie Broadband
Aussie Broadband prioritises delivering high-speed, dependable NBN connections and exceptional local customer support. It also offers a 4G connection backup on its plans.
Take a look at Aussie Broadband plans today.
Belong
One of the most affordable NBN internet service providers, Belong is perfect for those who are on a tight budget. There are no lock-in NBN plan contracts with its unlimited data plans, so you can cancel anytime.
Compare Belong plans and contact us for more.
Dodo
Dodo offers a great range of internet plans with unlimited data, including fixed wireless connections. It's also one of the few internet services that allow subscribers to bundle electricity and gas bills with internet bills.
Contact our team about Dodo plans today.
Exetel
Exetel offers both NBN and OptiComm plans with a focus on low costs and customer care. It also offers plans you can bundle with VoIP calls.
Reach our team about Exetel’s plans and get connected.
More Telecom
More Telecom offers various customisation options on its range of NBN plans, including add-on packs that can enhance your experience with additional features such as cloud storage and higher speed limits.
Compare More Telecom plans to learn more.
Optus
As Australia's second-largest NBN plan provider, Optus offers a range of perks for its customers, like discounted movie tickets and special events. Its NBN plans include unlimited data with no lock-in contracts.
Optus plans are available to connect to today - call our team for more.
Superloop
Superloop NBN plans provide great typical evening speeds for a very reasonable price. You can choose BYO modem or rent one of its NBN-ready modems for a small additional fee.
Take a look at Superloop’s plans and get connected.
Tangerine
Tangerine Telecom offers NBN services to residential and commercial customers, including fixed wireless. Customers can freely switch plans or cancel their service anytime without additional plan fees.
Compare Tangerine’s plans and get signed up.
Telstra
Telstra is Australia's oldest and largest fixed broadband provider. It offers a range of benefits to NBN customers, including three free data top-ups per year, a Telstra Air membership, Telstra TV, and Telstra Device Security. It also offers 4G backup on its plans.
Talk to our team about Telstra’s plan range today.
TPG
TPG offers NBN plans at speeds from 12Mbps to 250Mbps and lets you bring your own modem.
Connect with our team to learn more about TPG plans today.
How to switch NBN providers
Transitioning to a new NBN provider is a straightforward process. At Compare Broadband, we're here to assist you every step of the way.
Simply get in touch with one of our broadband experts via our hotline, and we'll guide you in finding the perfect plan for your requirements and ensuring a seamless connection.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you select the ideal plan:
-
Explore your options: Take your time to research and compare different NBN plans to find the one that suits your household best.
-
Look out for special deals: Many NBN providers offer limited-time promotions, so be sure to shop around for potential savings.
-
Sign up online: Once you've identified the right plan, complete the online sign-up process with your new provider.
-
Await the switch: Your new provider will handle the transition, typically taking just a few hours without any service interruptions.
-
Confirm with your old provider: Following the switch, your old provider should stop billing automatically, but you can also verify by reaching out to their customer support.
How much does it cost to switch NBN plans?
Switching NBN plans between providers typically does not cost anything other than the monthly fee. However, additional charges may be in place if you're signing up for a new provider, require an NBN technician, or need extra equipment to connect.
To get a same-day NBN service connection, choose an NBN service provider that can accommodate your request. Keep in mind that this service is available only if NBN has previously been connected at the property you're looking to connect.
At Compare Broadband, call us today and get a same-day connection. Our broadband experts will ensure your same-day NBN service connection is a seamless experience.
FAQs
How do I find out my NBN connection type?
You can determine your NBN connection type by visiting the official NBN website. You also can use our search engine tool above or call our broadband experts. You may also contact your current service provider to learn more about the available NBN technology type in your area.
Can I get my NBN plan bundled with my phone?
Many providers offer phone bundling options, which offer discounts and savings when both services are under a single account. Some NBN providers also offer credits for phone calls or mobile phone SIM plans.
Do I need a new modem for an NBN plan?
It depends. If you are switching between NBN providers and already have an NBN capable modem, you should be able to use that. However, your new ISP may not offer you detailed support on how to set it up correctly. If you are changing NBN technologies during a move, for example, you will most likely need to purchase a new modem. Service providers usually offer modems for sale or give you the option to bring your own.
Am I eligible for a free fibre upgrade from the government?
Visit our fibre upgrade page and enter your address to check for eligibility.
NBN Plans
NBN Connection Types
NBN Providers
Internet Plans in Australia
NBN guides
- Ultimate NBN guide
- NBN Rollout Map
- How to upgrade your NBN to FTTP?
- How Much Does NBN Installation Cost?
- How to Switch NBN Providers
- What NBN Speed do I Need?
- Why is My NBN Slow?
- NBN Outages: What to do During an Outage
- Your Definitive Guide Around The NBN Connection Box
- How to Check NBN Speed?
- Tips for faster NBN
- How long to set up NBN connections?
- Does my building have NBN?
- How to find your NBN Node
- NBN Providers with 4G backup














 Loading...
Loading...
